Longevity Nutrition: The Golden Rules of Healthy Aging
Longevity Nutrition: The Golden Rules of Healthy Aging
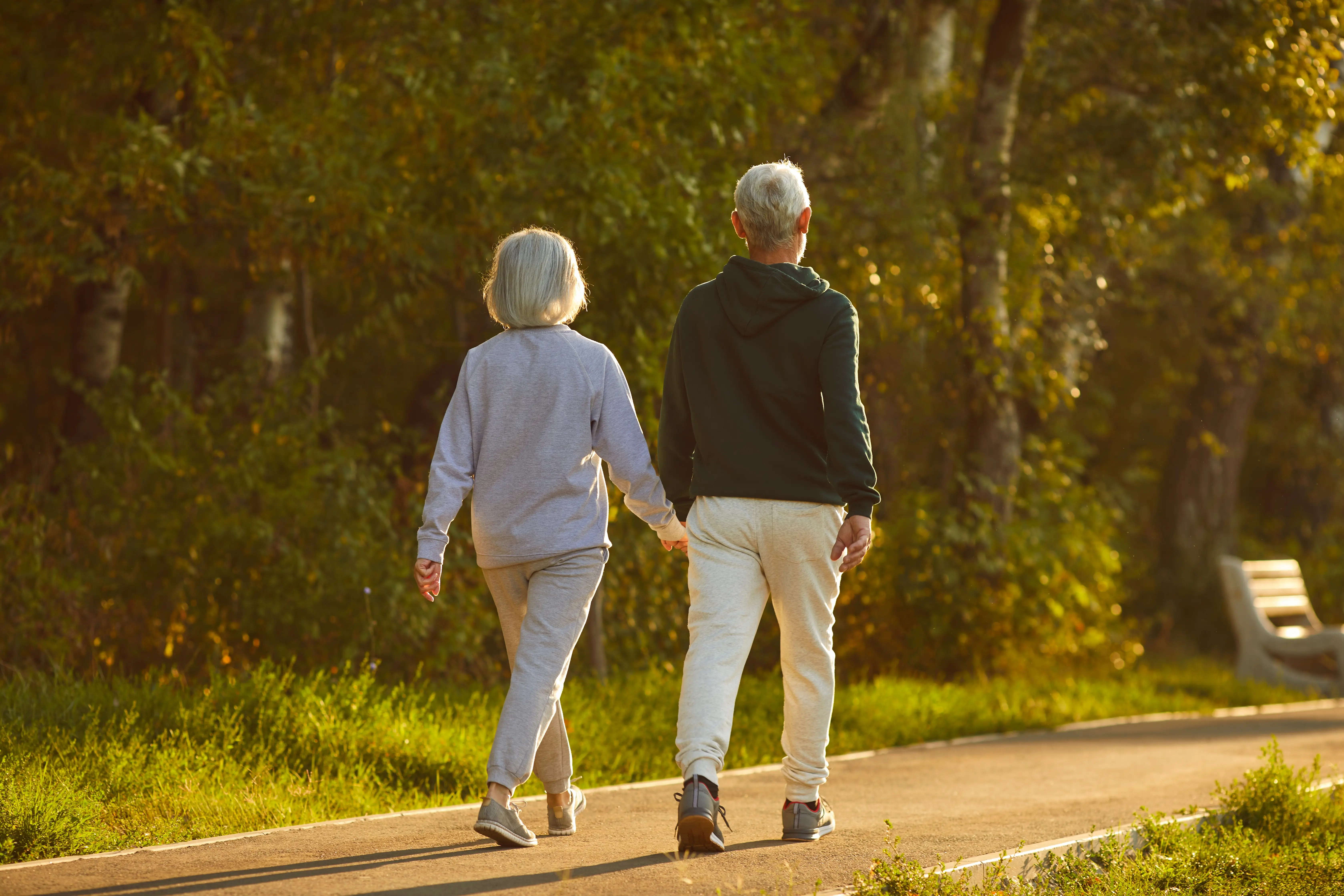
If longevity runs in your family, your odds of living a longer life are higher. However, genetics is only one factor; the lifestyle choices you make play a major role in your ability to live longer, maintain good health, and keep doing the activities you enjoy.
What is longevity?
Longevity refers to living a long life. Experts believe that genetics accounts for roughly 25% of the differences in human lifespan, while the remaining variation is largely influenced by how we care for our bodies.
And that matters because longevity is about more than just living longer. Most of us don’t simply want to extend our years — we want to enjoy a high quality of life as we age.
There are straightforward steps you can take to stay healthy, active, and productive throughout your life. The secrets to potentially reaching 100 years or more include maintaining a nutritious diet, engaging in regular exercise, and making positive lifestyle choices.
How good nutrition promotes longevity?
What you consume directly affects the cells in your body, which in turn influences overall longevity.
A nutritious diet supplies cells with essential energy sources and helps maintain their stability and proper function. Consuming healthy foods supports immune cells that protect against infections and other health threats, shields other cells from damage, and assists the body in repairing or replacing damaged cells.
Conversely, a diet rich in sugar and unhealthy fats can make cells more susceptible to damage and dysfunction throughout the body. This may increase the risk of infections, cancer, inflammation, and chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
An effective dietary approach for promoting longevity is a plant-based diet. Research has revealed that women who most closely followed a plant-based Mediterranean diet — emphasizing vegetables (except starchy vegtables like potatoes), fruits, nuts, whole grains, legumes, and fish, while minimizing red and processed meats — had a 23% lower risk of death from any cause compared to those who did not adhere closely to this eating pattern.
A plant-focused diet emphasizes consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Plant-based foods are rich in antioxidants like beta-carotene, lycopene, and vitamins A, C, and E, which help protect cells from damage.
Following a plant-based approach doesn’t require you to become completely vegetarian or eliminate meat or desserts entirely. Rather, it means that the majority of your daily food intake should be minimally processed and primarily derived from plants.
The Role of Exercise in Supporting Longevity
Numerous studies indicate that regular physical activity promotes longer life due to its wide-ranging positive effects on the body. These benefits include stronger heart and lung function, healthier blood vessels, increased muscle strength, improved balance, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Being physically active can reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, diabetes, and falls, among other advantages. Collectively, these effects contribute to a longer lifespan. Exercise can also enhance mood and improve sleep quality.
How much activity is needed to support health and longevity?
- 150 minutes a week of moderate activity, or
- 75 minutes a week of vigorous movement, or
- an equivalent combination of both intensities.
Other Lifestyle Habits That Support Longevity
Beyond healthy eating and regular physical activity, several lifestyle habits can significantly influence both lifespan and quality of life.
- Prioritize sleep: Consistently getting good-quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being and may even help extend life. Chronic sleep deprivation can increase the risk of long-term health problems affecting the heart, brain, lungs, immune system, and more. Experts generally recommend that adults aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night.
- Stay hydrated: A study of over 11,000 adults found that those who maintain proper hydration tend to be healthier, develop fewer chronic conditions such as heart and lung disease, and may live longer than those who do not.
- Maintain social connections: Research involving 28,000 participants demonstrated a strong link between social activity and longevity. People who engage socially more frequently tend to have longer survival, with higher levels of socialization correlating with greater chances of living longer.
- Adopt a positive mindset: Surprisingly, your outlook on life may influence lifespan. Two recent studies found that optimism was associated with longer life in women across diverse racial and ethnic groups and with improved emotional health in older men. These findings suggest that positive thinking can offer meaningful benefits for longevity.
REFERENCES:
- Harward Health Publishing,2024,Longevity: Lifestyle strategies for living a healthy, long life