Water Lentils: A Sustainable Superfood for the Future
Water Lentils: A Sustainable Superfood for the Future
What Are Water Lentils?
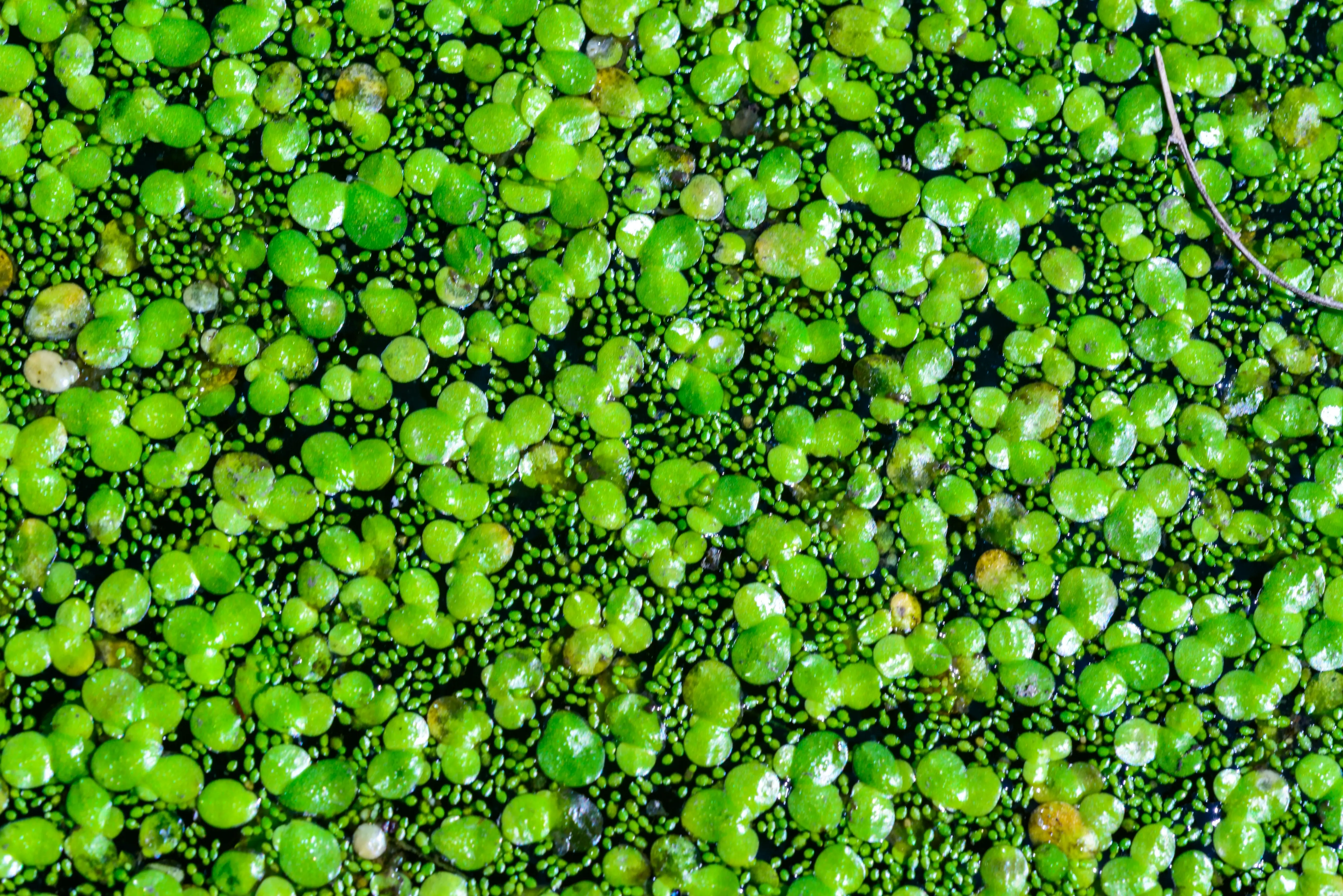
Water lentils, also known as duckweed, are small, floating aquatic plants that grow in freshwater environments. Despite their tiny size, they are packed with nutrients, making them a promising food source for the future. These plants are rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals, and their rapid growth allows for high yields with minimal environmental impact.
Unlike traditional crops, water lentils do not require farmland to grow. They thrive in controlled environments on water surfaces, making them an efficient and sustainable food option. In regions facing land scarcity or climate challenges, water lentils could play a key role in ensuring food security.
The Nutritional Benefits of Water Lentils
Water lentils are a powerhouse of nutrients, offering numerous health benefits:
- High Protein Content: Water lentils contain up to 45% protein in dry weight, making them comparable to soy and other plant-based protein sources. They provide all essential amino acids, making them a complete protein—ideal for vegetarians and vegans.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals: These tiny plants are packed with essential nutrients such as iron, calcium, and magnesium. They also contain vitamin B12, which is rare in plant-based foods, making them especially valuable for those on a vegan diet.
- Supports Gut Health: Water lentils contain fiber and prebiotics, which promote a healthy gut microbiome. This can aid digestion and support overall well-being.
- Antioxidant Properties: With a high content of polyphenols and carotenoids, water lentils have antioxidant effects that help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases.
Why Are Water Lentils Important?
The global food system is facing increasing challenges, including land scarcity, climate change, and the need for more sustainable protein sources. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recently approved water lentils for consumption in the EU, following nearly ten years of extensive research led by Wageningen University & Research (WUR). This approval marks a significant step in the protein transition—a shift toward plant-based proteins to reduce environmental impact.
According to research associate Ingrid van der Meer, one of the leading experts on water lentils, these plants offer multiple advantages:
- High Nutritional Value: Water lentils contain a substantial amount of protein, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutrient-dense food source.
- Efficient Growth: Their exponential growth rate allows for high yields in a small space, especially when cultivated in stacked layers.
- Sustainability: Since they grow on water, no agricultural land is required, reducing deforestation and soil degradation.
- Low Resource Consumption: They require less water and fewer inputs compared to traditional crops.
How Will Water Lentils Be Used?
Now that water lentils have received approval, the focus shifts to consumer acceptance and industry adoption. Researchers and food innovators are exploring various ways to incorporate them into everyday diets:
- Fresh or Frozen: Water lentils can be packaged as fresh greens or processed into frozen cubes for convenience.
- Incorporated into Foods: They can be added to dishes like pesto, pasta (e.g., ravioli), plant-based burgers, and pakora.
- Restaurant Introductions: Some chefs have started experimenting with water lentils in their recipes, helping familiarize consumers with the taste and benefits.
The Future of Water Lentils
Despite their many advantages, the success of water lentils as a mainstream food product will depend on consumer awareness and industry collaboration. Food manufacturers, retailers, and restaurants must work together to introduce water lentils in an appealing and accessible way.
With ongoing research into packaging, storage, and new culinary applications, experts predict that water lentils could become a common supermarket item within the next three years. Their potential to contribute to a more sustainable and nutritious food system makes them an exciting development in the future of plant-based nutrition.
Source:
Wageningen University and Research : Water lentils authorised for production and consumption in EU
https://www.wur.nl/en/newsarticle/water-lentils-authorised-for-production-and-consumption-in-eu.htm